Take the most commonly used single-piston rod double-acting cylinder in pneumatic systems as an example. The typical structure of the cylinder is shown in Figure 1 below. It consists of cylinder barrel, piston, piston rod, front end cover, rear end cover and seals. The interior of the double-acting cylinder is divided into two chambers by the piston. A cavity with a piston rod is called a rod cavity, and a cavity without a piston rod is called a rodless cavity.
When compressed air is input from the rodless cavity, the rod cavity is exhausted,CylinderThe force formed by the pressure difference between the two chambers acting on the piston overcomes the resistance load and drives the piston to move. , causing the piston rod to extend;when the rod cavity takes in air and the rodless cavity exhausts, the piston rod retracts. If the rod cavity and the rodless cavity alternately intake and exhaust air, the piston will achieve reciprocating linear motion.
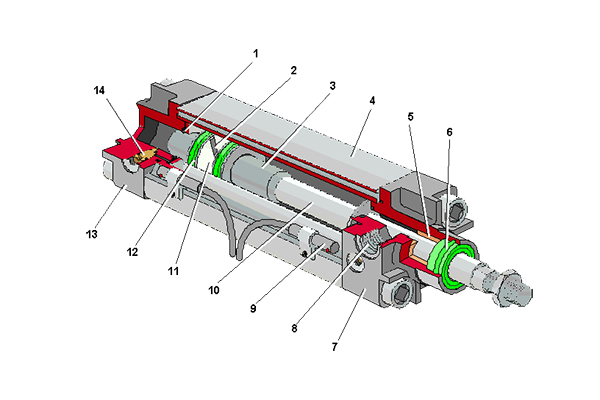
1, 3-buffer plunger 2-piston
4-Cylinder 5-Guide sleeve
6-Dust ring 7-Front cover
8-Air port 9-Sensor
10-piston rod 11-wear ring
12-Sealing ring 13-Rear end cover
14-Buffer throttle valve






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578