(2) Stepper motor and ball screw drive
The driving method of the ball screw has the characteristics of [1] directly converting the rotary motion of the motor into linear motion, [2] the pitch of the ball screw acts as a reduction device, and the transmission efficiency of the driving force and the efficiency of the motor are high.
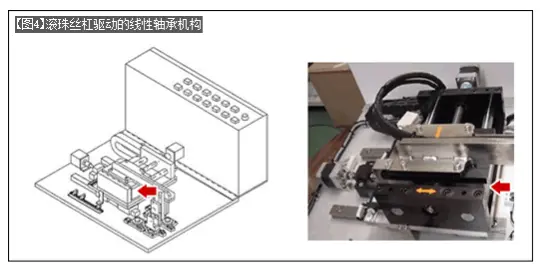
[Figure 4] is a drive mechanism with a linear bearing and ball screw structure for the Y-axis. Usually used in institutions that require unit feed or positioning accuracy requirements
■Supplementary instructions
a) Characteristics of stepper motors
・Stepper motors have the characteristics of large torque in the low speed range (large torque occurs during startup and deceleration), and are suitable for occasions where the moving distance is short and multi-point positioning control is required.
b) Necessary motor accuracy required to achieve target positioning accuracy
・Required positioning accuracy = ±0.01 (mm), when selecting the ball screw lead = 10 (mm/rev), the necessary accuracy (grading) of the stepper motor can be calculated by the following formula.
![]()
(3) Cylinder drive
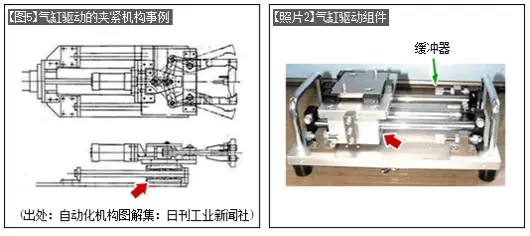
[Figure 5] is an example of a cylinder drive bearing in a clamping mechanism, and [Photo 2] is an example of a magnetic coupling type cylinder drive mechanism. Both use linear bearings (arrows) for guidance.
The cylinder drive cannot control the speed when starting and stopping, and it is necessary to use a buffer to reduce the impact when stopping. ([Photo 2]).
(4) Vertical guidance example
The guide in the vertical direction can be achieved by using flanged linear bearings. The linear bearings can be firmly installed without a specific support structure to achieve a compact and simple structural design (in the case of sliding guide rails, fixed guide rails are required vertically mounted base plate).

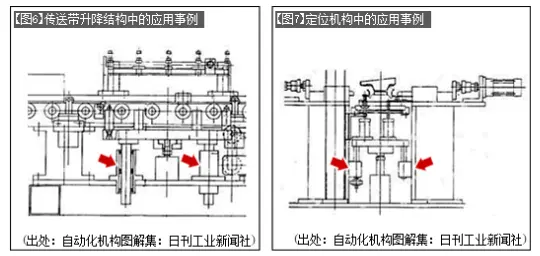
Similar to the structure of [Photo 4], the lifting guide ([Figure 6]) and positioning mechanism ([Figure 7]) at the lower part of the conveyor belt also use flange-type linear bearing structures.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578