Let’s reorganize the characteristics of linear bearings and explain them as follows:
1. Low price, medium performance linear guide bearing. (High cost performance)
2. The friction coefficient is small and the driver is easy to select. (Low-price cylinder type or mid-price motor type)
3. Combined with the synchronous belt, a structural design of silent and lightweight driving can be achieved.
4. In the case of vertical guidance, a simple and compact structural design can be achieved due to the center of gravity drive method
The following explains the use methods and characteristics of linear bearings through application examples on simple automation equipment.
(1) Stepper motor and synchronous belt drive
The timing belt drive structure has the advantages of quietness, light weight, low price, and no need for oiling. For the XY2-axis worktable, the usual design idea is to make the upper Y-axis lighter and reduce the load on the lower X-axis motor. For this reason, the Y-axis mostly uses a synchronous belt structure.
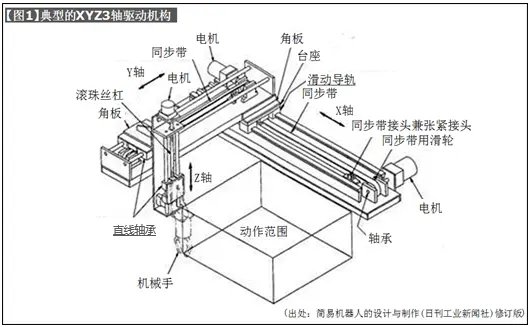
a) [Figure 1] shows a typical XYZ 3-axis drive mechanism.
The X-axis is a linear guide, and the Y-axis and Z-axis adopt linear bearing structures. The driving method adopts synchronous belt and ball screw.
b) [Photo 1] is an example of Y-axis application of IC chip transfer equipment. The Y-axis direction is converted into reciprocating motion through the timing belt.

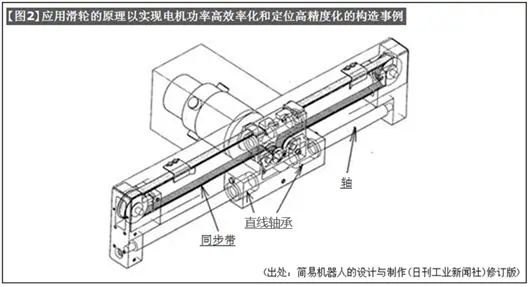
c) [Figure 2] is an application example of a single-axis robot with the following characteristics.
1. Two linear bearings are used across large spans to improve load-bearing performance and guidance accuracy.
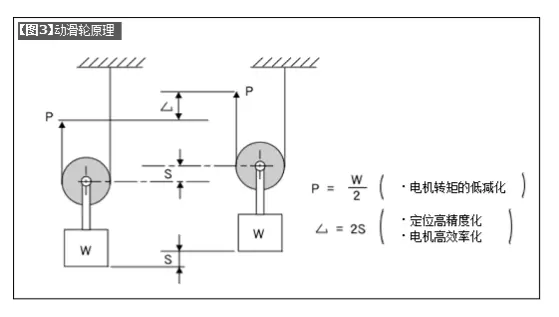
2. The design structure of the synchronous belt and pulley adopts the moving pulley principle ([Figure 3]), which achieves high efficiency of motor power and high positioning accuracy.
3. Using synchronous belt drive, it is lightweight and silent.
4. The synchronous belt and the shaft are arranged in parallel up and down. Even with a single-axis structure, the relative rotation of the shaft and the linear bearing can be controlled.







 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578