Here, we introduce an overview of the cutting-edge technology of linear guides that are much more precise than sliding guides.
Key components of products that display high-definition images, such as LCD screens for mobile phones and monitors for PCs, require sub-micron tolerance accuracy (for example, 0.3 μm or less). Many of these key components are made from ultra-precision metal molds and then mass-produced. For the processing of such ultra-precision metal molds, ultra-precision processing equipment that can achieve sub-micron accuracy is used.
Representative linear guide for ultra-precision processing equipment< /span>
The linear guide structure of ultra-precision processing equipment can be divided into the following two types.
a) Contact sliding guide・・・・The track is in contact with the movable body and moves.
b) Non-contact sliding guide・・・The track and the movable body move in a non-contact state.
(a) About contact sliding guide
·[Photo 1] shows a typical contact sliding guide structure used in ultra-precision processing equipment. A skilled worker performs a scraping operation ([Photo 2]) through manual finishing, and the result is a V-groove-shaped sliding guide. This guide is equipped with ultra-precision roller bearings.
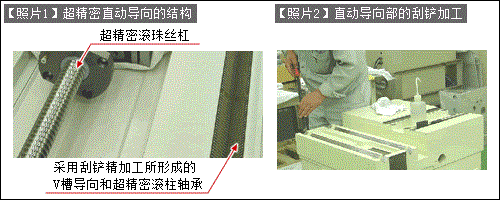
· Roller bearings and an upper movable body are installed on the V-groove guide formed by finishing using the scraper method, and accuracy is measured using measuring instruments to continuously reduce errors. This operation is repeated.
· The structure of this linear guide is driven by a ball screw. However, in order to avoid errors in the up, down, left and right directions caused by the deflection of the ball screw, the ball screw nut is fixed with a parallel spring and only transmits thrust in the linear direction.
(b) About non-contact sliding guide
·【Photo 3】is a picture of the appearance of an air bearing using granite stone used for precision platforms as structural materials.
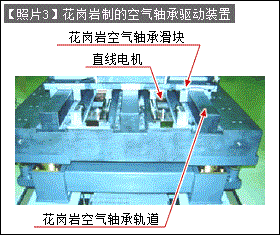
· Granite stone is a natural material, so changes over the years can be ignored. Insensitive to thermal deformation and absorbs vibration. It was selected due to the existence of this type of properties.
· The function of the air bearing is to release air in a gap of about 6μm, and use this air pressure to form an ultra-precision linear guide in a non-contact state.
· The direct-acting guide track is a convex block, and its final accuracy is also polished by manual polishing.
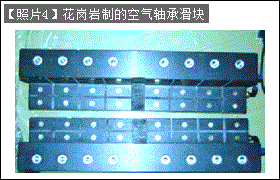
· The air cushion design of the movable part is important for air rigidity and avoiding resonance ([Photo 4])
·The silver cuboid in [Photo 3] is a linear motor.
· A completely non-contact sliding guide is formed by using air bearings and linear motors.
In this world of ultra-precision drive control, environmental control such as stable control of ambient temperature (for example, ±0.1°C), independent infrastructure to completely isolate external vibration, and dust-free environment are required.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578