The linear guide formed by the combination of the shaft and the linear bearing (or oil-free bushing) is composed of the simplest guide rail and slider. Here, the changes and characteristics of linear guides other than this structure are explained.
(1) Disadvantages of linear guides for shafts and linear bushings< /strong>
There are the following shortcomings.
| Composed of shaft guide + shaft + linear bushing< /td> | Countermeasures for shortcomings | Changes in direct-acting guidance |
| Linear bushings cannot rotate around the outer circumference of the shaft. | is composed of 2 axes to constrain the rotation. | Ball spline + spline shaft composition |
| Because it is in a hollow state without support, both ends become fixed Structural, therefore, if the mechanism is subjected to large vertical loads, it will result in insufficient rigidity. | Increase the shaft diameter and select a double-lined linear bearing< /span> | Composed of shaft guide + shaft + linear bushing< /td> |
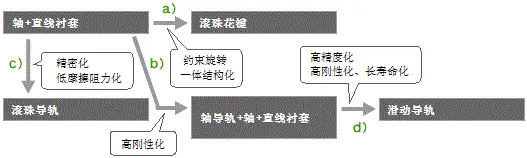
(2) Direct-action-oriented progress
The following simple diagram illustrates the progress of linear guides.
Simple explanation with diagrams.
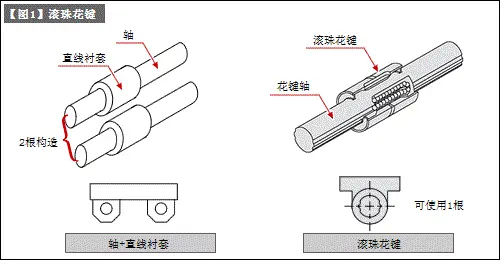
a) Ball splines are provided with rolling grooves for ball bearings on the shaft, and only linear motion is free. (Refer to [Figure 1])
b) Set a shaft guide rail on the hollow part of the shaft to improve the rigidity of the track. The structure formed by cutting this part with the matching linear bushing (refer to [Figure 2])

c) The free ball retainer is set as a bearing, so rotation and linear motion are not restricted.
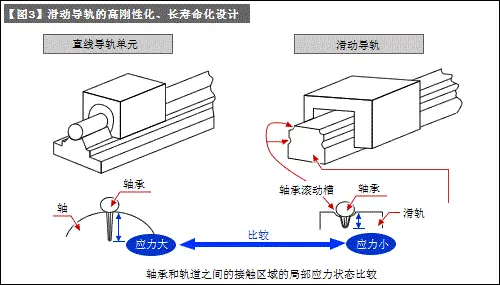
d) The basic structure is similar to b), but in order to improve the load resistance, a bearing rolling groove is provided to expand the contact area between the bearing and the track ( Refer to [Figure 3]).






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578