What is the function of the sensor on the cylinder? Cylinder sensors are mostly magnetic sensors (Hall switches), that is, the Hall switch outside the cylinder is fixed (but the Hall switch can be adjusted Hall switch position), the piston inside the cylinder is equipped with a magnetic ring (moves with the piston), when the magnetic ring on the piston moves to the Hall switch position, the Hall switch has a signal output and sends out the in-position signal.
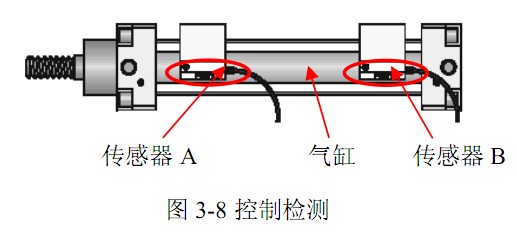
Working principle of cylinder sensor:A magnetic switch or other switch sensor can be installed on the cylinder. Its function is to sense the working status of the cylinder, so that the control circuit can receive the signal of the sensor switch to make the next step. action. For example: when the sensor switch is connected to the input end of the TPC8-8TD timing program controller, it can be used as an in-position stop, in-position start, in-position alarm, and an under-in-position alarm. and other position-related motion controls. The control function of the cylinder is realized by the induction switch and the controller. The specific functions can be set through the function setting table to set the required control functions. Such a combination Can realize the functions of various control devices.
The cylinder sensor is mainly used to detect the position of the piston in the cylinder. The user can install it directly in the cylinder for use. As a detection device, the sensor is the primary link in realizing automatic control and automatic detection. It can meet various user requirements for equipment information transmission, processing, storage, recording, display and control.
In recent years, cylinder sensors have become increasingly miniaturized and intelligent. Digital, multi-functional and systematic characteristics. Cylinder is the cavity in the internal combustion engine cylinder where the piston is placed. It is the track on which the piston moves, in which the gas burns and expands. It can also dissipate part of the explosion waste heat transmitted by the gas through the cylinder wall, so that the engine can maintain a normal operating temperature.







 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578