The function of the cylinder
Converts the pressure energy of compressed air into mechanical energy, and the driving mechanism performs linear reciprocating motion, swinging and rotating motion.
1. The cylinder is a cylindrical metal part that guides the piston to perform linear reciprocating motion in the cylinder. The working medium converts thermal energy into mechanical energy through expansion in the enginecylinder;the gas is compressed by the piston in the compressor cylinder to increase the pressure.
2. The casings of turbines, rotary piston engines, etc. are usually also called "cylinders". Application areas of cylinders: printing (tension control), semiconductors (spot welding machines, chip grinding), automation control, robots, etc.
Cylinder Principle< strong>
The movement speed of the cylinder is mainly determined by the needs of the driven working mechanism.
When the speed is required to be slow and stable, it is appropriate to use a gas-liquid damping cylinder or throttle speed regulation. The methods of throttling and speed regulation include: exhaust throttling is recommended for horizontal installation of thrust loads;air intake throttling is recommended for vertical installation of lifting loads;see the basic circuit section for specific circuits. The use of a buffer cylinder can prevent the cylinder from impacting at the end of its stroke. Usually, the buffering effect of the buffer cylinder is only obvious when the resistance load of the buffer cylinder is low and the speed is not high. If the speed is high, there will often be a shock at the end of the stroke.
Cylinder Structure
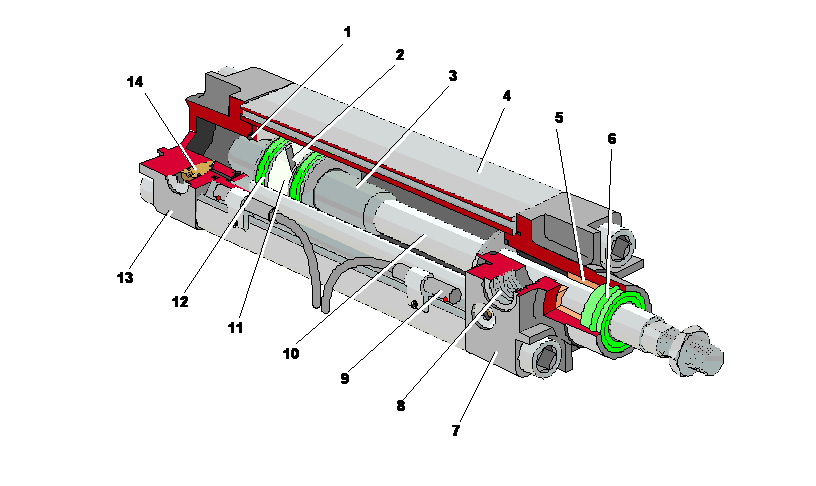
1. 3-buffer plunger 2-piston 4-cylinder 5-guide sleeve 6-dust ring 7-front cover 8-air port 9-sensor 10-piston rod 11-Wear-resistant ring 12-Sealing ring 13-Rear end cover 14-Buffer throttle valve
1. Cylinder tube
The inner diameter of the cylinder barrel represents the output force of the cylinder. The piston must reciprocate smoothly in the cylinder, and the surface roughness of the inner surface of the cylinder should reach Ra0.8um. In addition to using high-carbon steel pipes, the cylinder barrel material is also made of high-strength aluminum alloy and brass.
2. End cap
The end cover is provided with intake and exhaust openings, and some also have a buffer mechanism inside the end cover. The rod side end cover is provided with a sealing ring and a dust ring 6 to prevent air leakage from the piston rod and external dust from mixing into the cylinder. A guide sleeve 5 is provided on the rod side end cover to improve the guiding accuracy of the cylinder.
3. Piston
The piston is the pressurized part in the cylinder. In order to prevent the left and right chambers of the piston from passing air to each other, a piston sealing ring 12 is provided. A wear-resistant ring 11 is also provided to improve the guideability of the cylinder.
4. Piston rod
The piston rod is the most important force-bearing part in the cylinder. Usually high carbon steel is used, with hard chromium plating on the surface, or stainless steel is used to prevent corrosion and improve the wear resistance of the sealing ring.
5) Buffer plunger, buffer throttle
There are buffer plungers 1 and 3 on both sides of the piston along the axis direction. At the same time, there are buffer throttle valves 14 and buffer sleeves 15 on the cylinder head. When the cylinder moves to the end, the buffer plungers enter the buffer sleeve,CylinderExhaust required After the buffer throttle valve, the exhaust resistance increases, generating exhaust back pressure, forming a buffer air cushion, which plays a buffering role.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578