Finger cylinder is also a pneumatic actuator and it is also a modified cylinder. It can be used to grab objects and realize various actions of the manipulator.
Finger cylinder structure diagram
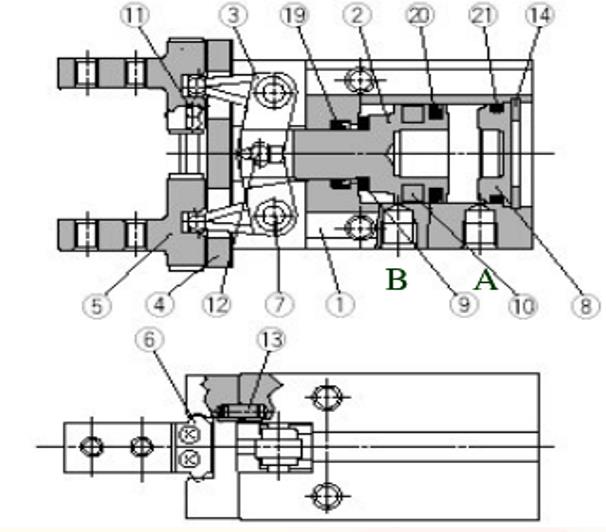
This picture isFinger cylinderStructure schematic diagram. When port A takes air in and port B exhausts, the cylinder piston rod 2 stretches out and rotates around the lever shaft 7 through the lever 3, driving the two fingers 5 to make an outward linear motion on the guide rail 4 through a set of steel balls 11. Then open. Release the work piece. The stop block 6 limits the finger opening stroke, and the positioning pin 13 ensures that the linear guide rail is not in position.
Finger Cylinder< strong>Tips for maintenance and upkeep
1. When the cylinder is inspected and reassembled, the parts must be cleaned, especially to prevent the sealing ring from being cut or damaged, and pay attention to the installation direction of the dynamic sealing ring.
2. During use, you should regularly check whether there are any abnormalities in various parts of the cylinder, whether there are loose connections in the joints, etc. The movable parts of the installed cylinder should be lubricated regularly. Oil.
3. When the cylinder is removed and not used for a long time, all processed surfaces should be coated with anti-rust oil, and the inlet and exhaust ports should be blocked with dust.
4. When the cylinder is inspected and reassembled, the parts must be cleaned and dirt must not be brought into the cylinder. In particular, the sealing ring must be prevented from being sheared and damaged and attention must be paid to the dynamic sealing ring. installation direction.
5. Develop a monthly, quarterly and annual maintenance system for the cylinder. You can refer to the content stipulated in the directional valve maintenance management system.
Finger Cylinder< strong>Experiences from installation to process performance
1. Choose parallel opening and closing type or fulcrum opening and closing type according to the size, shape, quality and purpose of use of the work.
2. Select the series of air grippers according to the size, shape, overhang, usage environment and purpose of the workpiece.
3. Select the air claw according to the size of the particles held by the air claw, the distance between the clamping points, the amount of extension and the stroke. Cylinder size.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578