Basic structural design of cylinder
The cylinder is the main part of the piston compressor that makes up the compressor volume. According to conditions such as the pressure, displacement, compressor structural plan, type of compressed gas, material used to make the cylinder, and the habits of the manufacturer, The structure of the cylindercan take many forms, but the design of the cylinder is mainly:
1. It should have sufficient strength and stiffness, and the working surface should have good wear resistance;
2. There must be good cooling and the working surface should be in a good lubrication state;
3. Reduce the clearance volume and gas resistance in the cylinder as much as possible;
4. The connection and sealing of the combined parts must be reliable;
5. It must have good manufacturing process performance and be easy to disassemble and assemble;
6. The cylinder diameter and valve seat mounting hole and other dimensions should comply with the "three modernizations" requirements.
In order to ensure working reliability, all cylinders in the compressor row must have high concentricity. For this reason, the cylinder is generally provided with positioning shoulders. The guide surface of the positioning shoulder should be concentric with the working surface of the cylinder, and the joint plane should be perpendicular to the center line. Since the piston and piston rings slide on the working surface of the cylinder, the working surface of the cylinder is subject to wear. When the piston is at the dead center position, the speed is equal to zero. The specific pressure of the first piston ring on the compression volume side is very large, and there is It may bite into the work surface, so the wear is greatest there.
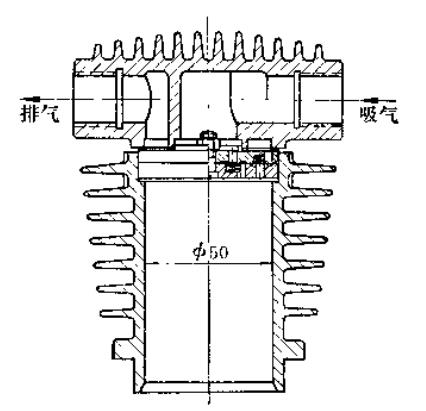
Therefore, the hardness and fit between the piston ring and the cylinder working surface should be appropriately selected. In this design, a fine pearlite structure is added to the working surface of the cylinder, with a hardness of over HB170, making the hardness of the piston ring 10HB~20HB higher than that of the cylinder working surface. The wear is minimal when the working surface roughness reaches 0.1, but it is difficult to achieve such roughness using ordinary processing methods. Therefore, the surface roughness of the compressor without crosshead in this design is not less than 0.4.
The arrangement of the valves on the cylinder has a great influence on the structure of the cylinder. The key to designing the air valve this time is that the channel cross-section should be large, the clearance volume should be small, and installation and repair should be convenient. Therefore, a reed valve was selected for this design. In order to simplify the structure of the cylinder, the air valve is installed on the cylinder head. The center line of the air valve is parallel to the center line of the cylinder. The air valves are arranged on both cylinder heads. At this time, the clearance volume caused by the communication channel between the air valve and the cylinder is small, and the air flow is smooth.
The lubrication point of the single-acting cylinder is arranged in the middle of the sweep distance of the first piston ring on the compression volume side, and the cylinder generally has an indicator connection. In order to prevent gas leakage, the end of the compression bolt is tightened with a closing nut, and the heating plate seals the joint surface between the nut and the valve cover. The suction valve is affected by the gas pressure in the cylinder, and the force that separates from its seat is much greater than the same force exerted by the exhaust valve. Therefore, the compression bolts of the suction valve pressure cover are larger than those of the exhaust valve. , this design uses cylinderThe material is HT200 gray cast iron.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578