When the diaphragm pump is working, the crank connecting rod mechanism drives the plunger to reciprocate under the drive of the motor. The movement of the plunger passes through the working liquid (usually oil) in the cylinder. ) is transmitted to the diaphragm, causing the diaphragm to move back and forth.
The cylinder head part of the pneumatic diaphragm pump is mainly composed of a diaphragm to separate the transported liquid and the working liquid. When the diaphragm moves toward the transmission mechanism, the pump cylinder is negative when working. When the diaphragm moves to the other side, the liquid is discharged. The transported liquid is separated from the working liquid by the diaphragm in the pump cylinder, and only contacts the pump cylinder, suction valve, discharge valve and the pump side of the diaphragm, but does not contact the plunger and sealing device. This makes the column Important parts such as plugs work completely in oil medium and are in good working condition.
Diaphragm pump is a special form of positive displacement pump. It relies on the back and forth agitation of a diaphragm to change the volume of the working chamber to absorb and discharge liquid.

Structure and composition of diaphragm pump
The diaphragm pump is mainly composed of two parts: the transmission part and the diaphragm cylinder head. The transmission part is the driving mechanism that drives the diaphragm to move back and forth. Its transmission forms include mechanical diaphragm metering pump, hydraulic transmission and pneumatic transmission. Among them, the most widely used one is hydraulic transmission. The picture shows a hydraulically driven diaphragm pump. The working part of the diaphragm pump mainly consists of a crank connecting rod mechanism (not shown in the picture), plunger, liquid cylinder, diaphragm, pump body, suction valve and discharge valve, among which the crankshaft connection The driving mechanism composed of rod, plunger and hydraulic cylinder is very similar to that of a reciprocating plunger pump.
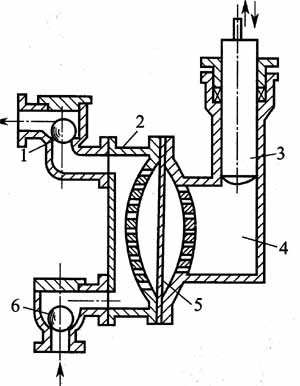
1-discharge valve;2-pump body;3-plunger;4-liquid cylinder;5-diaphragm;6-suction valve.
Precautions for using diaphragm pumps
1. Ensure that the largest particles contained in the fluid do not exceed the maximum safe passing particle diameter standard of the pump.
2. The inlet pressure should not exceed the maximum allowable operating pressure of the pump. Compressed air higher than the rated pressure may cause personal injury and property loss and damage the performance of the pump.
3. Ensure that the pump pressure pipeline system can withstand the highest output pressure achieved and ensure the cleanliness and normal working conditions of the drive air system.
4. Static sparks may cause explosions, resulting in personal casualties and property losses. Use wires with a large enough cross-sectional area as needed to properly and reliably ground the grounding screw on the pump.
5. Grounding requirements comply with local regulations, legal requirements and some special requirements on site.
6. Fasten the pump and each connecting pipe joint to prevent static sparks caused by vibration, impact and friction. Use antistatic hose.
7. Periodically check and test the reliability of the grounding system, and the grounding resistance is required to be less than 100 ohms.
8. Maintain good exhaust and ventilation, and keep away from flammable, explosive and heat sources.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578