Slide cylinder refers to a cylindrical metal part in which the cylinder guides the piston to perform linear reciprocating motion. The air is in thecylinderThermal energy is converted into mechanical energy through gradual expansion;the gas is compressed by the piston in the compressor cylinder and the pressure is increased. Cylinders are generally used in fields such as printing, semiconductors, automation control, and robotics.

The working principle of the slide cylinder
Input compressed air into the cylinder on the fixed mold. The guide rod is pushed by the cylinder at one end and pushed in the opposite direction. The pushing stroke depends on the length of the guide rod. . Pneumatic slide cylinders are generally used for transportation of precision instruments, with relatively high accuracy. The guide rod cylinder has strong lateral load resistance. Determine the push and pull forces on the piston rod based on the amount of force required for the job. Therefore, the cylinder should be selected so that the output force of the cylinder has a slight margin. If the bore diameter is selected to be small, the output force will be insufficient and the cylinder will not work properly;but if the bore diameter is too large, it will not only make the equipment bulky and costly, but also increase air consumption, resulting in a waste of energy. When designing the clamp, a force-increasing mechanism should be used as much as possible to reduce the size of the cylinder.
Structure diagram of slide cylinder
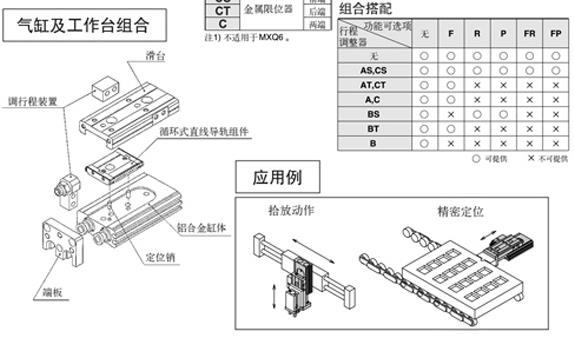
Characteristics of slide cylinder
The piston of the cylinder is fixed on the piston rod. There are plates at both ends of the piston rod that can be firmly fixed on the machine table. The slide table moves back and forth on the piston rod. This is what we Slide cylinders commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
In ProgressSlide cylinderWe need to understand three aspects when selecting the model: 1. The steps for selecting the slide cylinder model;2. The corresponding calculation formula. Chart;3. Selected example
Steps for selecting slide cylinder model
1. Conditions of use: Consider the installation posture, workpiece shape, and list the conditions of use.
2. Kinetic energy:
1) Find the kinetic energy E(J) of the concentrated load.
2) Find the allowable kinetic energy Ea(J).
3) Confirm that the kinetic energy of the concentrated load does not exceed the allowable kinetic energy.
3-1 Loading rate of concentrated load mass: Find the allowable concentrated load mass Wa (kg). Find the load rate of concentrated load mass α1.
3-2 Load rate of static moment: Find the static moment M (N.m). Find the allowable static moment Ma (N.m). Find the load rate α2 of static moment. .
3-3 Load rate of dynamic moment: Find the dynamic moment Me (N.m);Find the allowable power moment Mea (N.m);Find the load rate of the power moment α3.< /span>
3-4 The sum of load rates: The sum of load rates does not exceed 1 and can be used.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578