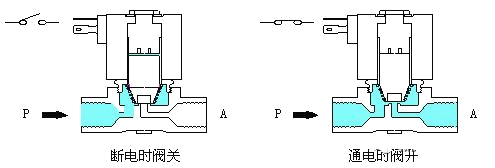
1. Direct-acting solenoid valve
Principle: When the power is on, the solenoid valve coil generates electromagnetic force to lift the closing member from the valve seat, and the valve opens;when the power is off, the electromagnetic force disappears and the spring force presses the closing member. On the seat, the valve is closed. Features: It can work normally under vacuum, negative pressure and zero pressure, but the diameter generally does not exceed 25mm.
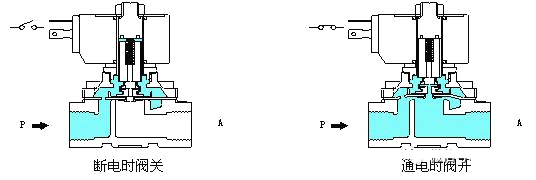
2. Step-by-step direct-acting solenoid valve
Principle: It is a principle that combines direct operation and pilot operation. When there is no pressure difference between the inlet and outlet, after power is supplied, the electromagnetic force directly connects the pilot small valve and the main valve. The valve closing parts are lifted upward in turn, and the valve opens. When the inlet and outlet reach the starting pressure difference, after power is turned on, the electromagnetic force first opens the pilot small valve, the lower pressure of the main valve increases, and the upper chamber pressure decreases, thereby using spring force or medium pressure to push the closing member downward to close the valve. . Features: It can operate reliably at zero pressure, vacuum, and high pressure, but the power is large and it must be installed horizontally.
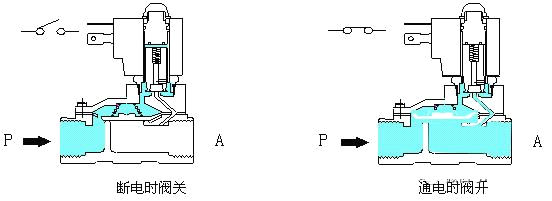
3. Pilot solenoid valve
Principle: When energized, the electromagnetic force opens the pilot hole, and the pressure in the upper chamber drops rapidly, forming an upper, lower, and higher pressure difference around the closing member. The fluid pressure pushes the closing member to move. , the valve opens;when the power is off, the spring force closes the pilot hole, and the inlet pressure quickly enters the upper chamber through the bypass hole, forming a lower pressure difference and a higher pressure around the valve closing member. The fluid pressure pushes the closing member to move downward and close. valve. Features: The upper limit of the fluid pressure range is relatively high and can be installed arbitrarily (customization is required) but the fluid pressure difference condition must be met.
The working principle of solenoid controlled reversing valve
In the pneumatic circuit, the function of the electromagnetic control reversing valve is to control the opening and closing of the air flow channel or change the flow direction of the compressed air. The main working principle is to use the electromagnetic force generated by the solenoid coil to push the valve core to switch and realize the reversal of air flow. According to the different ways of pushing the reversing valve by the electromagnetic control part, it can be divided into direct-acting solenoid valve and pilot-operated solenoid valve. Direct-acting solenoid valves directly use electromagnetic force to push the valve core to change direction, while pilot-operated reversing valves use the pilot air pressure output from the solenoid pilot valve to push the valve core to change direction.
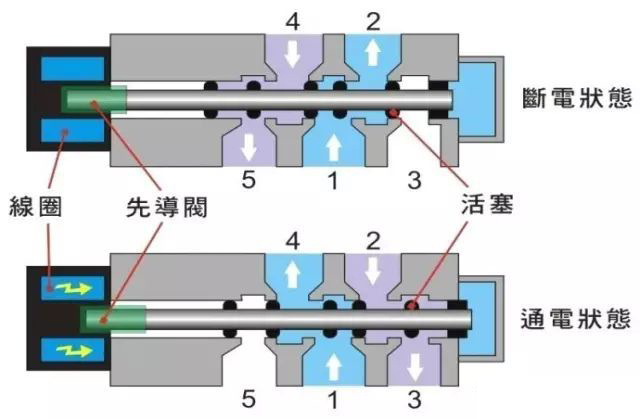
The working principle of the two-position five-way double electric control solenoid valve
(five-way, two-position) direct-acting< span style="color:#4C33E5;">A simple cross-sectional view and working principle of the solenoid valve (normally off type) structure. In the initial state, 1 and 2 air intake;4 and 5 exhaust;when the coil is energized, the static iron core generates electromagnetic force to move the pilot valve, and the compressed air enters the valve pilot piston through the air path to start the piston. In the middle of the piston, the seal The round surface opens the channel, 1, 4 air intake, 2, 3 exhaust;when the power is cut off, the pilot valve resets under the action of the spring and returns to its original state.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578