What is swap To the solenoid valve?
Reverse The abbreviation of solenoid valve is solenoid valve, which uses electromagnet suction to control the movement of the valve core. To achieve reversal. The solenoid valve consists of a slide valve and an electromagnet.
According to different power sources, electromagnets can be divided into two types: AC electromagnets and DC electromagnets.
According to whether the armature of the electromagnet is immersed in oil, electromagnets can be divided into dry type and wet type.
Advantages, disadvantages and applications of reversing solenoid valves:
It moves quickly, is easy to operate, and is easy to realize automatic control. Due to the limitation of the size of the electromagnet, the electromagnetic force is limited and can only be used in systems with small flow rates.
Working principle of reversing solenoid valve
There is a movable spool inside the valve. There is an electromagnet on each side of the valve. When one side is powered, the spool is affected by the electromagnetic force. When the iron moves to that side, the other side will be open. When there is a power outage, the valve core will return to the center by the spring. Whether there is a passage in the middle depends on its neutral function. O type is blocked, H type is passage, etc.
The reversing solenoid valve adopts wet AC or DC solenoid. Solenoid valve controls the different working positions of the valve core through electromagnets. When the solenoid is de-energized, the valve core is held in the middle or end position by spring pressure (except for pulse valves). When the electromagnet is energized, the valve core is pushed to the working position, and returns to the initial state after the power is turned off. At this time, pushing the fault check button by hand can move the valve core.
Since the inside of the wet electromagnet is connected to the oil return chamber, the movement of the armature oil can reduce wear and buffering, improve heat dissipation performance, and extend service life. AC electromagnets have the characteristics of short action time, simple electrical control circuit, and no need for special contact protection. DC electromagnets have soft switching characteristics, high operating frequency, are not sensitive to overload or low voltage response, and work reliably.
1) Two digits and three Pass the electromagnetic reversing valve
When the power is off: P→A B is blocked.
When power is on: P→B A is blocked.
2) Three-position four-way electromagnetic directional valve
When the electromagnets are all powered off: P, A, B, and T are all disconnected.
When the left electromagnet is energized: P→A, B→T.
When the electromagnet at the right end is energized: P→B, A→T.
Reversing solenoid valve structure
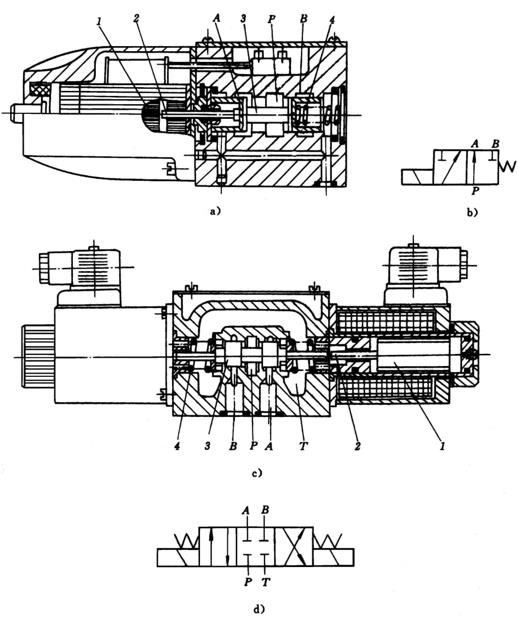
The above isWorking principle of reversing solenoid valve, structure of reversing solenoid valve Content introduction, if you want to know more related information, you can Log in to www.diancifa.cc to view.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578