2. Maximum air consumption rate: When the cylinder piston moves at maximum speed, the amount of air consumed per unit time (under standard atmospheric pressure)
Maximum air consumption of the cylinder: Q=piston area x piston speed x absolute pressure
The commonly used formula is: Q=0.046D2v (p+0.1)
Q------Maximum air consumption of the cylinder under standard conditions (L/min)
D------Bore diameter of cylinder (cm)
v------Maximum speed of cylinder (mm/s)
p------Using pressure (MPa)
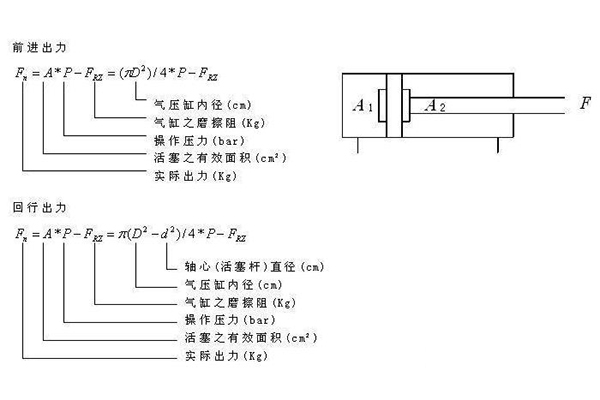
The air consumption of the cylinder can be divided into maximum air consumption and average air consumption.
The maximum air consumption is the air consumption required when the cylinder moves at maximum speed, which can be expressed as:
qr=0.0462D^2*um(P+0.102)
For example, the cylinder diameter D is 10cm, the maximum speed is 300mm/s, and the operating pressure is 0.6Mpa, then
The maximum air consumption of the cylinder qr=0.046*10^2*300*(0.6+0.102)=968.76(L/min), so the cv value is 1.0 or the effective cut-off A solenoid valve with an area of about 18mm can meet the flow requirements.
If the operating pressure of the cylinder is 0.5Mpa and the maximum speed is 200mm/s, the maximum air consumption of the cylinder is qr=553.84.
If the cylinder diameter D is 5cm, the maximum speed is 300mm/s, and the operating pressure is 0.6Mpa, the maximum air consumption of the cylinder is qr=242.19, so the cv value should be about 0.3 That’s it.
PS: Unofficial empirical formula: maximum air consumption = cylinder diameter (in cm) squared multiplied by a coefficient of 10 (at this time, the operating pressure is 0.6MPa, and the maximum speed is 300mm/s )
The average gas consumption isThe air flow consumed by the cylinderin one working cycle of the pneumatic system. It can be expressed as:
qca=0.0157(D^2*L+d^2*ld)N(p+0.102)
上style中
qca: average air consumption of the cylinder, L/min (ANR);
N: The working frequency of the cylinder, that is, the number of reciprocating cycles of the cylinder per minute, one reciprocating is one week, cycle/min;
L: cylinder stroke, cm;
d: Inner diameter of the pipe between the reversing valve and the cylinder;cm
ld: the length of the pipe, cm.
For example, a cylinder with a cylinder diameter D of 100mm (10cm) and a stroke L of 100mm (10cm) has an operating frequency N of 60 cycles/min, d=10mm (1cm), ld =60mm (6cm),
qca=0.0157(D^2*L+d^2*ld)N(p+0.102)=0.0157*(10^2*10+1^2*6 ))*60*(0.6+0.102)=666.5251704L/min(ANR).
Average air consumption is used to select air compressors and calculate operating costs. The maximum air consumption is used to select air treatment components, control valves and piping sizes, etc. The difference between the maximum air consumption and the average air consumption is used to select the tank volume.






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578