What is a double-acting cylinder
Can apply force on both sides of the piston to control its active movementCylinder strong>It’s called double action. A typical driving cylinder, such as a steam locomotive, can take in air and output force in both directions. The cylinders of modern internal combustion engines are single-acting, because only the top of the piston is equipped with an intake and exhaust system. When the piston is moving upward, it cannot be output. It may seem that double action saves space and structural materials, but in fact this is not the case. Because it must keep the piston rod and cylinder parallel, this results in an extremely large and complex structure. Therefore, after the steam engine era passed, this mechanism was no longer used in power devices. For actuators, bidirectional action can apply force in both directions, either pushing or pulling, which has practical benefits. For example, the main cylinder on a modern hydraulic press is generally bidirectional. At the same time, the return stroke piston cross section is occupied by a certain area by the piston rod, causing the output force to be smaller than when outputting from the top of the piston. This also brings certain benefits: the return stroke speed is greatly accelerated.
Double-acting cylinder structure principle:
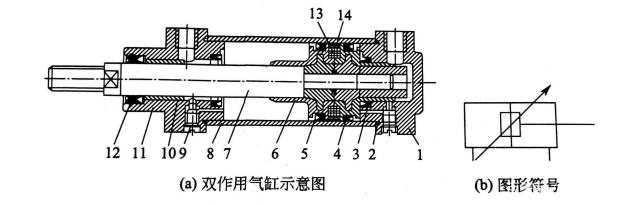
1-Rear cylinder head;2-Sealing ring;3-Buffer sealing ring;4-Piston sealing ring;5-Piston;6-Buffer plunger;7-Piston rod ;8-cylinder barrel;9-buffer throttle valve;10-guide sleeve;11-front cylinder cover;12-dust seal;13-magnet;14-guide ring
Ordinary double-acting cylinders generally consist of cylinder barrels, front and rear cylinder heads, pistons, piston rods, seals, fasteners and other parts. The cylinder barrel is fastened and locked by 4 tie rods and nuts between the front and rear cylinder heads. There is a piston connected to the piston rod in the cylinder, and a piston sealing ring is installed on the piston. To prevent air leakage and the intrusion of external dust, the front cylinder head is equipped with a piston rod sealing ring and a dust ring. This double-acting cylinder is divided into a rod cavity (referred to as the head cavity or front cavity) and a rodless cavity (referred to as the tail cavity or rear cavity) by the piston.
Precautions for using double-acting cylinders:
Double-acting cylinders are not equivalent to double-rod cylinders. Affected by the piston rod, the thrust generated by the rodless cavity is greater than the thrust generated by the rod cavity. Large (the force of pushing out the piston rod is greater than the force of retracting the piston rod), which needs to be considered when designing the pneumatic circuit.
During use: the normal lubrication of the cylinder must be ensured. The lubricator on the pneumatic triplet must not cut off the oil to avoid premature wear of the piston cylinder (some imported cylinders are damaged due to the piston Pre-coated with grease, it can work with oil-free lubrication, but once the cylinder has been lubricated, it must be ensured that the lubrication continues and the lubrication cannot be interrupted).
Double-acting cylinders require the use of clean compressed air, Cylinder When using raw material tape to seal the joint, it must be ensured that it can only be wrapped around the threaded part of the joint to prevent raw material tape debris from clogging the air holes. .






 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578