2. According to the principle, solenoid valves are divided into three categories: direct-acting, distributed direct-acting, and pilot-operated;according to the structure, they are divided into two categories: diaphragm type solenoid valve and piston type solenoid valve.
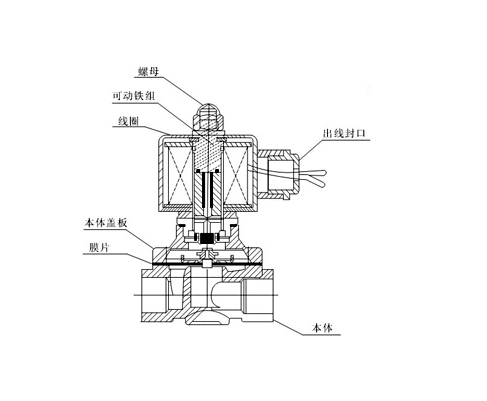
3. Working principle of solenoid valve: There is a closed cavity in the solenoid valve. There are through holes at different positions, and each hole leads to a different oil pipe. There is a valve in the middle of the cavity, and two electromagnets on both sides. Whichever side of the magnet coil is energized, the valve body will be attracted to that side. By controlling the valve body Move to block or leak different oil drain holes, and the oil inlet hole is always open, the hydraulic oil will enter different oil drain pipes, and then push the piston of the oil cylinder through the oil pressure, and the piston drives the piston rod, and the piston The rod drives the mechanical device to move. In this way, the mechanical movement is controlled by controlling the current of the electromagnet.
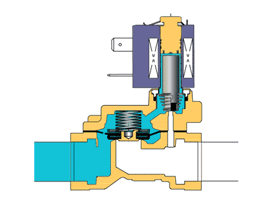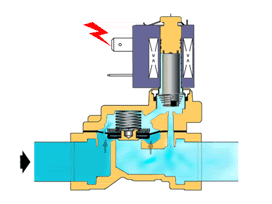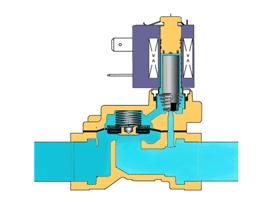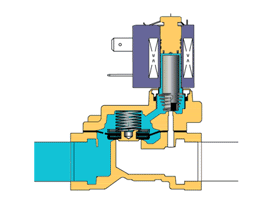
4. Working principle of direct-acting solenoid valve:
When the power is turned on, the solenoid coil generates electromagnetic force to lift the closing member from the valve seat, and the valve opens;when the power is turned off, the electromagnetic force disappears, and the spring presses the closing member against the valve seat, and the valve closes.
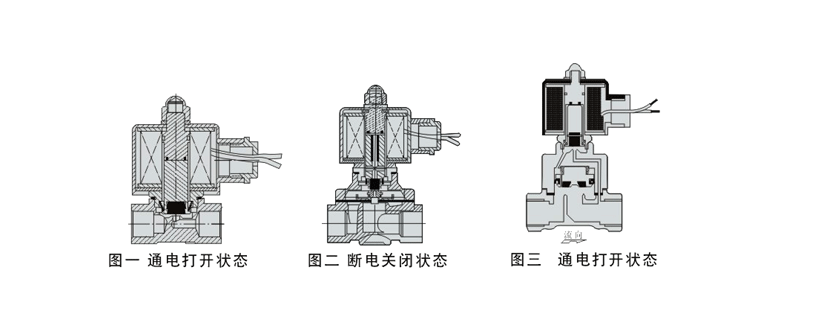
5. Working principle of distributed direct-acting solenoid valve:
It is a principle that combines direct action and pilot action. Normally closed type---when there is no pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet, the electromagnetic force directly opens the pilot hole and connects the main valve piston upwards after energization, and the valve opens;when the inlet and outlet reach the starting pressure difference, after energization, the electromagnetic force first When the pilot hole is opened, the pressure in the upper chamber of the main valve piston drops, thereby using the pressure difference and electromagnetic force to pull the main piston, and the valve port opens;when the power is turned off, the pilot hole is closed by spring reset, and the upper chamber of the main piston is pressurized, pushing the main piston downward. Move and the valve closes. Normally open is the opposite of normally closed.
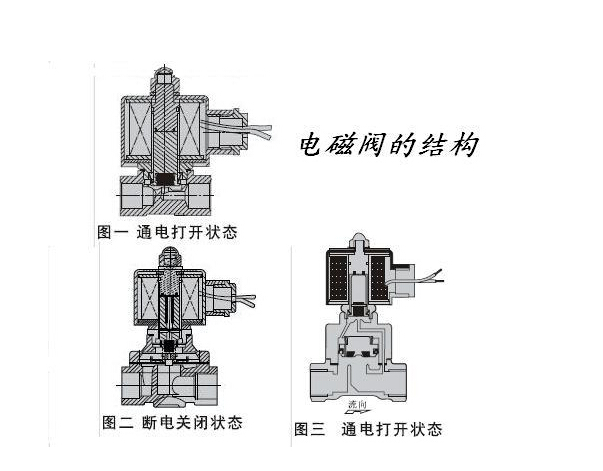
6. Working principle of pilot solenoid valve:
Normally closed type---when energized, the electromagnetic force attracts the pilot hole valve core, the pilot hole opens, and the pressure in the upper chamber of the main valve piston drops, forming an upper and lower pressure in the upper and lower chambers of the main piston, so that the pressure in the lower chamber pushes The main piston opens the valve;when the power is off, the spring force resets and closes the pilot hole, and the upper chamber of the main piston is pressurized, forming an upper and lower pressure in the upper and lower chambers of the main piston. The medium pressure and spring force push the main piston and the valve closes. . Normally open is the opposite of normally closed.
7. Working principle of diaphragm solenoid valve:
When the power is turned on, the electromagnetic force opens the pilot hole, and the pressure in the upper chamber drops rapidly, forming an upper, lower, and higher pressure difference around the closing member. The fluid pressure pushes the closing member to move upward, and the valve opens;when the power is turned off, the spring force closes the pilot hole. , the inlet pressure passes through the bypass hole and quickly forms a pressure difference between the lower and upper parts around the valve closing part. The fluid pressure pushes the closing part downward to close the valve.
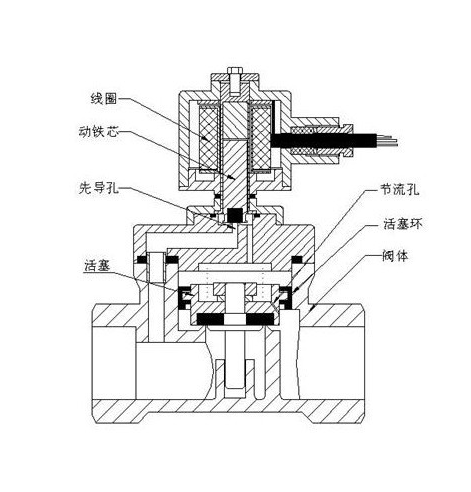
8. Working principle of piston solenoid valve:
After the coil is energized, due to the suction effect, the moving iron core moves down, pressing down the valve plug of the auxiliary valve, closing the auxiliary valve, and the pressure in the main valve cup rises. When the pressure rises to a certain value, the upper and lower pressure differences of the main valve cup are the same. , due to the electromagnetic force, the moving iron core loses its position under the main valve cup, presses the main valve seat, and the valve closes. When the coil is powered off, the electromagnetic suction force is zero, the auxiliary valve plug and the support core are lifted upward due to the action of the spring, the auxiliary valve opens, and the fluid on the main valve cup flows away through the auxiliary valve, reducing the impact on the main valve cup. When the pressure on the main valve cup is reduced to a certain value, the pressure difference is used to push up the main valve cup, the main valve opens, and the medium flows.







 WhatsApp: +8615857777578
WhatsApp: +8615857777578